Urban Water Modeling
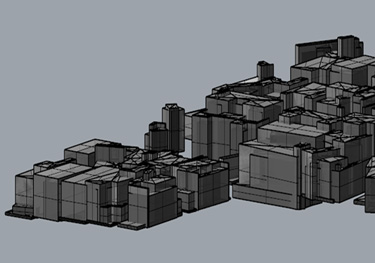
In this project we develop an integrated modeling workflow to evaluate all water, food and energy systems generation and consumption at an individual building level within an urban neighborhood.
Key performance indicators help observers correlate costs, carbon emissions and jobs associated with, for example, hydroponic food production versus photovoltaic proliferation. One case study used data from a neighborhood in Riyadh where smart meter water usage was already being collected. Simultaneously analyzing water, energy and food consumption at the household level helps researchers hypothesize ways the three interrelated systems can be optimized to improve costs, lower carbon emissions and envision how to create jobs locally to sustain the system.

RESEARCH AREAS

Info & Decision

Systems Innovation
IMPACT AREAS

Agriculture

Urban Systems